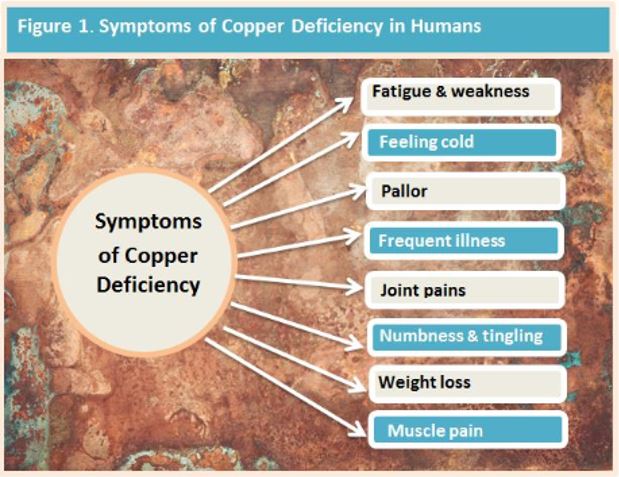
Signs & Symptoms of Copper Deficiency
InterClinical eNews June 2018, Issue 81
Copper has been recognised as an essential mineral since the mid 19th century when copper deficiency anaemia was first identified. In this issue we take a closer look at daily copper needs, the symptoms people with copper deficiency can experience, identify at-risk populations and discuss how the symptom picture can be easily mistaken for other conditions
Copper Requirements
The Australian national adequate daily intake (AI) for copper is currently set at 1.7 mg for men and 1.2 mg for women. (1) However, insufficient data exists to establish a recommended dietary intake (RDI) and some argue that the recommended intake should be set higher than the AI at 2.3 mg. (1) If this is correct and 2.3 mg represents a more accurate picture of requirements, then the intake of the vast majority of populations in developed countries appears to fall well below this level. If this is the case, subclinical copper deficiency may be a more common condition than previously anticipated. (1,2)
Copper Status
Copper status is influenced by a number of factors including dietary intake, age, physiological fitness, gastrointestinal health, and the level of copper antagonists and synergists and copper regulators such as riboflavin.(3)
At-Risk Populations
Certain segments of the population require higher levels of copper. These segments include: women during pregnancy and lactation, those with impaired gastrointestinal health such as Crohn’s Disease, IBS, IBD, Coeliac Disease, those on refined western diets and bariatric surgery patients. Induced copper deficiency is also on the increase ostensibly due to the use of zinc-based denture adhesives and sustained high dose zinc supplementation above 45 mg per day. (4,5)
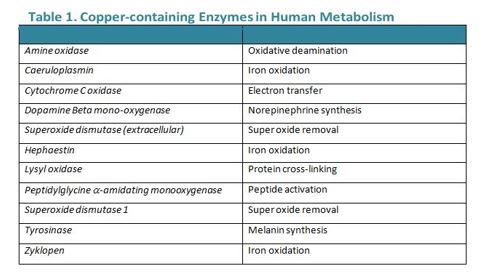
Copper Enzymes
Copper is an integral component of several enzymes in the body. A cursory look at the roles of these copper-containing enzymes indicates why a deficiency can produce conditions such as anaemia, pancytopenia and/or myelodysplastic syndrome (see Table 1. below). Common symptoms may include: impaired energy production, abnormal glucose and/or cholesterol metabolism, augmented oxidative damage, increased iron accumulation in tissues, alterations in the structure and function of circulating immune and blood cells, disordered neuropeptide production and processing, weakened cardiac muscular contractility, and unrelenting neurobehavioural effects. (6) Hypocupraemia may also affect the function of 54 copper-binding proteins within which help to regulate the transport and distribution of copper throughout the body. (7)
Copper Deficiency Mistaken for Other Conditions
Copper deficiency can be easily mistaken for other conditions such as vitamin B12 or folate deficiency because they present with similar symptoms such as persistent non-iron anaemia and ataxia. (2). Other conditions that may mimic copper deficiency include myelodysplastic syndrome, aplastic anaemia and lymphoma affecting the bone marrow, therefore, it is important to consider in a differential diagnosis when other more obvious diagnoses prove fruitless. (2)
InterClinical Comment:
Marginal copper deficiency may be more common than previously anticipated in the population at large with far-reaching health implications. Hair Tissue Mineral Analysis is a quick, and easy way to help identify whether low copper might be an issue for you.
REFERENCES
- Bost M, Houdart S, Oberli M, Kalonji E, Huneau JF, Margaritis I. Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology. 2016;35:107-15.
- Prohaska JR. Impact of copper deficiency in humans. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2014;1314(1):1-5.
- Chen H, Kimura M, Itokawa Y. Changes in iron, calcium, magnesium, copper, and zinc levels in different tissues of riboflavin-deficient rats. Biological trace element research. 1997;56(3):311-9.
- Wazir SM, Ghobrial I. Copper deficiency, a new triad: anemia, leucopenia, and myeloneuropathy. Journal of community hospital internal medicine perspectives. 2017;7(4):265-8.
- Duncan A, Yacoubian C, Watson N, Morrison I. The risk of copper deficiency in patients prescribed zinc supplements. Journal of clinical pathology. 2015;68(9):723-5.
- Hordyjewska A, Popiołek Ł, Kocot J. The many “faces” of copper in medicine and treatment. Biometals. 2014;27(4):611-21.
- Blockhuys S, Celauro E, Hildesjö C, Feizi A, Stål O, Fierro-Gonzalez JC, Wittung-Stafshede P. Defining the human copper proteome and analysis of its expression variation in cancers. Metallomics. 2017;9(2):112-23.
Copyright InterClinical Laboratories 2018, 2020

No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.