Viruses, Nutritional Immuno-Modulators and Metabolic Types
The immune system is a complex network consisting of cells, tissues and organs and their coordination is required to protect the body from infectious pathogens or viruses and non- infectious foreign substances. It is essential for the immune system to be at its optimum for resistance to invading pathogens and for the development of immunity. Optimisation of the immune system depends upon many factors, not the least of which includes...
Calcium – Mastering Mineral Series 1
Calcium ranks fifth, after oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, in the mineral composition of the human body. It makes up 1.9% of the body by weight. We require an average daily positive calcium balance of 180 mg during the first 20 years of growth. Around 99% of total body calcium is located in the skeleton. The remaining 1% is distributed evenly between the teeth and soft tissues, with only 0.1%...
Sodium – Mastering Minerals Series 1
In this article we look at the latest research on sodium, including storage, and an individual’s ability to absorb it and utilise it independent of intake. Characteristics of sodium InterClinical eNews July, Issue 108 Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the earth’s crust and the second most abundant element in seawater. An adult human body contains about 250g of sodium and any excess is naturally excreted by the body. About 85%...
Chromium – Mastering Minerals Series 1
InterClinical eNews June 2020, Issue 107 Chromium is the eighth largest classical element in the earth’s crust.1 The human body’s total content is approximately 6 milligrams. 8 It is widely distributed in the atmosphere, soil, water, animals and plants in the form of chromite. Chromium is a biologically active element which is at its highest in body tissue at birth and declines with age. 8 The first major research on chromium in...
Selenium – Mastering Minerals: 10 Masterful Facts
Selenium is a naturally occurring metalloid element that is essential to both humans and animals in trace amounts. Of all the elements, selenium has one of the narrowest ranges between dietary deficiency and toxic levels. The status of populations, animals and crops varies markedly around the world.17 Se AbsorptionSelenium and Glutathione PeroxidaseSelenium and inflammatory diseasesSelenium and blood sugar regulationSelenium and ReproductionSelenium and the ThyroidSelenium and the LiverSelenium and DepressionSelenium and Cardiovascular...
Magnesium – Mastering Minerals Series 1
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant mineral and is essential for good health. Approximately 600 enzymes depend upon its presence in our body in sufficient amounts.1 It affects many cellular functions including the transport of potassium and calcium ions. As well, magnesium modulates signal transduction, energy metabolism and cell proliferation. Magnesium has a huge role in bone mineralisation, cardiovascular health and the nervous and neuromuscular systems. It participates in the metabolism...
Immune System Patterns in Hair Tissue Mineral Analysis
InterClinical eNews March 2020 Special Edition The wonder of our immune systemOur immune system is miraculous and complex. Research into how it functions reveals a sophisticated security system that constantly scans the body to identify and remove any threat to our well being. Receptors associated with the immune system are concerned with interrogating the environment for evidence of danger, infection or abnormal cell death. They are also present inside the cell where...
Nutrients and Herbs Supporting Immune System Health Against Viruses
InterClinical eNews March 2020 Special Edition What is a virus? Viruses vary widely in shape and complexity. They do not contain the chemical machinery needed to carry out chemical reactions for life. Instead a virus carries only nucleic acid, with a set of genetic instructions, and a coat of protein to protect it. Enveloped viruses have an extra surrounding covering made of a lipid membrane. A virus must have a host...
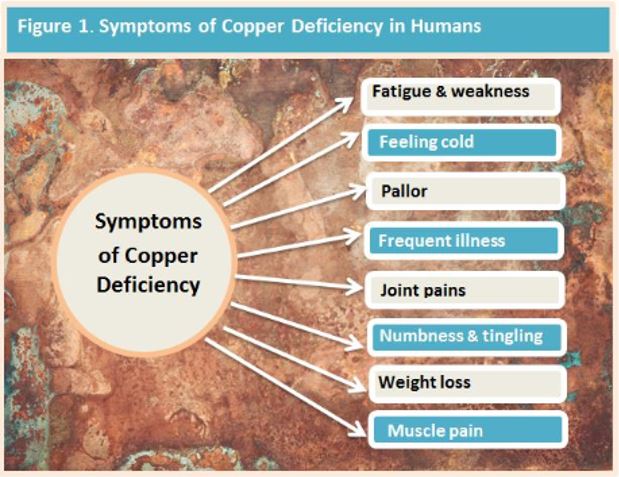
Copper Deficiency & Excess – Mastering Minerals 10 Masterful Facts
InterClinical eNews March 2020, Issue 102 Characteristics of CopperFactors Affecting Cu Homeostasis ScurvyLiver FunctionGenetic DisordersHigh Zinc Intake: Zn/Cu RelationshipCeruloplasmin and Citrate used in supplementsCopper Anemia Potassium Deficiency and CuCopper and dietBioavailabilityDetermining Cu statusConclusion REFERENCES Characteristics of Copper Copper is an essential micronutrient. The human body contains approximately 100 mg. It is a co-factor for many redox enzymes with ceruloplasmin being the most abundant Cu-dependent ferroxidase enzyme (with an important role in iron metabolism)....
Manganese – Mastering Minerals Series 1
InterClinical eNews February 2020, Issue 101 In this issue we examine one of the lesser known nutrients, Manganese. Although this is a trace element and is needed by the body in very small quantities, it is critical for good health. What is manganese’s role in good health? How do we know when to prescribe it? ‘A well-known professional basketball player was a devout vegetarian. He felt he performed better if he kept...